|
|
本文参考孙卫琴,杜聚宾所创作的 <<精通Vue.js: Web前端开发技术详解>>一书
为了在Vue项目中使用Axios,首先要安装Axios插件,还有可选的Vue-Axios插件。Vue-Axios插件能够把Axios与Vue更方便地整合在一起,允许组件通过this.axios的形式来访问Axios。
对于helloworld项目,在DOS命令行转到helloworld根目录下,运行以下命令,就会安装Axios和Vue-Axios插件:| npm install axios vue-axios |
在src/main.js中引入Axios和Vue-Axios插件,参见例程1。
例程1 main.js
import {createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import axios from 'axios'
import VueAxios from 'vue-axios'
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(router)
app.use(VueAxios,axios)
app.mount('#app') |
接下来在Vue组件的代码中就可以通过this.axios的形式来访问Axios了。
1. 异步请求例程2的GetCustomer.vue定义了GetCustomer组件,它根据用户输入的id,到服务器端查询匹配的customer对象,把它显示到网页上。
例程2 GetCustomer.vue
<template>
<div>
<p>输入id: <input v-model="customer.id" />
<button @click="getCustomer">查询</button> {{msg}} </p>
<p> {{isLoading}}</p>
<p>名字:{{customer.name}} </p>
<p>年龄:{{customer.age}} </p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return {
customer: {id: '', name: '', age: ''},
msg: '',
isLoading: ''
}
},
methods: {
getCustomer(){
this.customer.name=''
this.customer.age=''
this.msg=''
this.isLoading='正在查询...'
this.axios({
baseURL: 'http://www.javathinker.net',
url: '/customer',
method: 'get',
params: {id: this.customer.id}
}).then( (response)=> {
this.isLoading=''
if(response.data !== null){
this.customer=response.data
}else
this.msg='未找到匹配的数据!'
}).catch( (error) =>{
this.isLoading=''
console.log(error)
})
}
}
}
</script> |
在GetCustomer组件的getCustomer()方法中,通过axios()函数来发出Ajax请求:
this.axios({ //返回Promise对象
baseURL: 'http://www.javathinker.net',
url: '/customer',
method: 'get',
params: {id: this.customer.id}
}) |
以上axios()函数的参数是一个请求配置对象,在该请求配置对象中,baseURL属性表示根URL、url属性表示相对URL,method属性表示请求方式,params属性表示请求参数(也称为查询参数),以上代码也可以简写为:
this.axios
.get('http://www.javathinker.net/customer?id='+this.customer.id) |
在src/router/index.js中,为GetCustomer组件设置的路由的路径为“/getcustomer”。通过浏览器访问“http: //localhost:8080/#/getcustomer”,在网页的id输入框中输入1,然后点击“查询”按钮,会看到网页上先显示提示信息“正在查询...”,接下来再显示相应的customer对象的信息,参见图1。

图1 查询id为1的customer对象
如果在网页的id输入框中输入5,然后点击“查询”按钮,会看到网页上先显示提示信息“正在查询...”,接下来显示“未找到匹配的数据!”。
在GetCustomer组件的getCustomer()方法中,先把isLoading变量设为“正在查询...”,接下来再调用axios()函数。axios()函数会异步请求访问服务器:
this.isLoading='正在查询...'
this.axios({
……
}).then( (response)=> {
this.isLoading=''
……
}).catch( (error) =>{
this.isLoading=''
……
}) |
在浏览器与服务器进行异步通信的过程中,浏览器的主线程会继续运行,刷新网页上的{{isLoading}}插值表达式,显示当前值“正在查询...”。等到浏览器与服务器的通信结束,浏览器端接收到了响应结果,就会执行then()函数,把isLoading变量的值改为“”,并且如果response.data不为null,还会把response.data赋值给customer变量。Vue框架的响应式机制会同步刷新网页上的{{isLoading}}、{{customer.name}}和{{customer.age}}插值表达式。
Promise对象的then()函数的返回值仍然是Promise对象,它会异步执行then()函数的参数指定的函数。以下代码表面上看,是把响应正文显示到网页上:
<template>
<div>{{content}} </div>
</template>
<script>
……
mounted(){
let result={}
this.axios.get('http://www.javathinker.net/customer?id=1')
.then(response=>{
result=response.data
})
this.content=result
}
……
</script |
实际上,以上代码中的赋值语句的执行顺序为:
let result={}
this.content=result
result=response.data |
因此,网页上的{{result}}表达式的值始终为{}。2.POST请求方式例程3的Calculate.vue定义了Calculate组件,它会把用户输入的变量x和变量y通过POST请求方式传给服务器,服务器返回x+y的运算结果,Calculate组件再把运算结果显示到网页上。
例程3 Calculate.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<p>输入变量x: <input v-model.number="x" /> </p>
<p>输入变量y: <input v-model.number="y" /> </p>
<button @click="add">计算</button>
<p>{{result}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return {
x: 0, y: 0, result: ''
}
},
methods: {
add(){
this.axios.post( //采用POST请求方式
'http://http://www.javathinker.net/add',
'x='+this.x+'&y='+this.y //请求正文
).then( response=> {
this.result=this.x+'+'+this.y+'='+response.data
}).catch( error =>{
console.log(error)
})
}
}
}
</script> |
GetCustomer组件的add()方法通过axios.post()函数来指定请求方式为POST,该函数等价于以下axios()函数:
this.axios({
baseURL: 'http://www.javathinker.net',
url: '/add',
method: 'post', //指定POST请求方式
data: 'x='+this.x+'&y='+this.y //请求正文
}) |
在src/router/index.js中,为Calculate组件设置的路由的路径为“/calculate”。通过浏览器访问“http: //localhost:8080/#/calculate”,在网页的变量x和变量y的输入框中分别输入数字,然后点击“计算”按钮,add()方法就会请求服务器计算x+y,再把运算结果显示到网页上,参见图2。
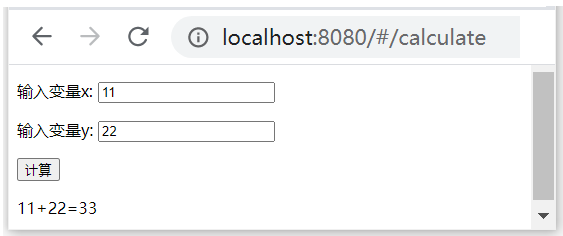
图2 Calculate组件的网页
程序猿的技术大观园:www.javathinker.net
|
|